A B E X
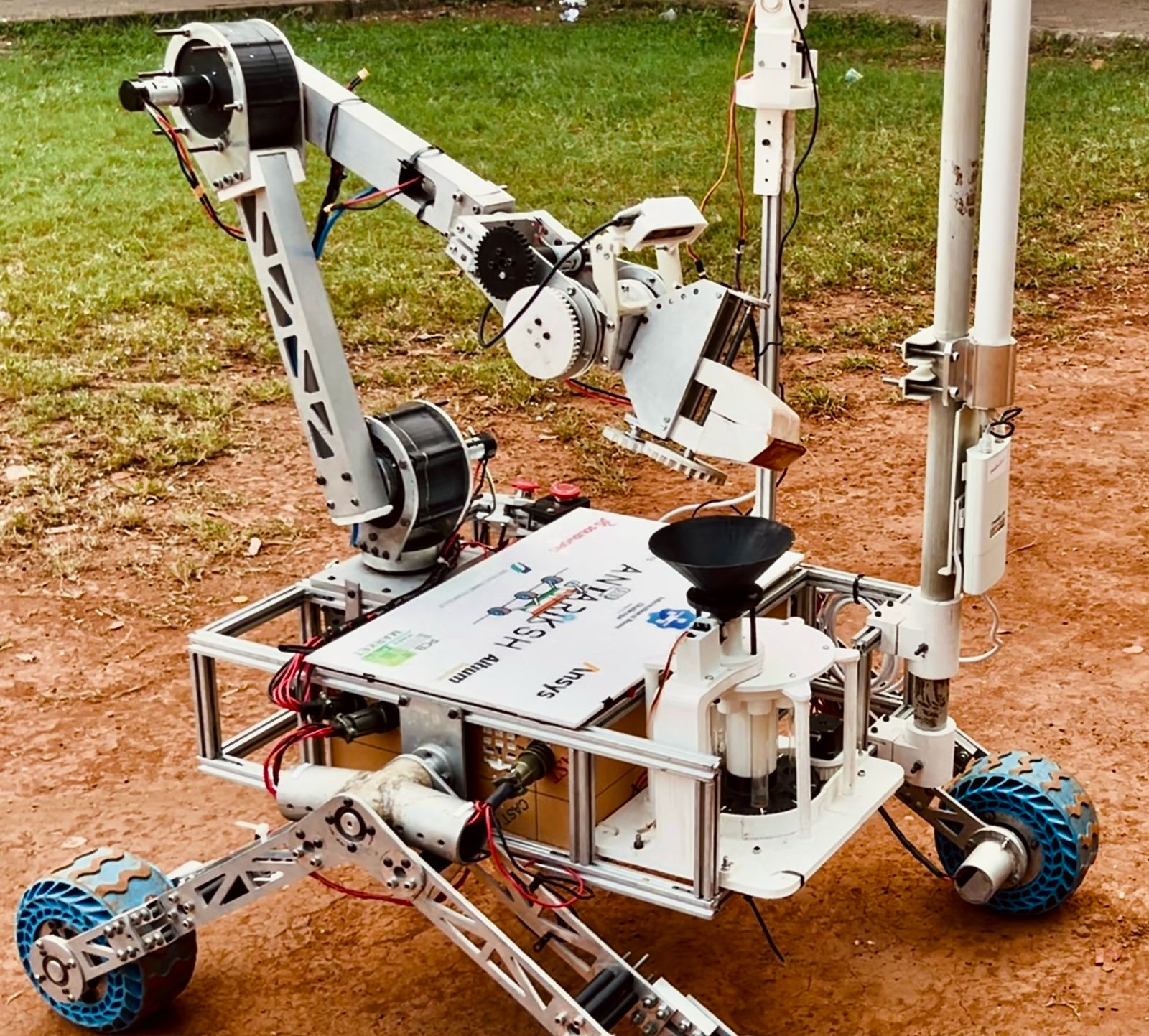
The rover will serve as a mobile science lab to investigate Martian-like sites for signs of extinct or extant life. The rover must be equipped with at least one instrument or assay capable of detecting life, chosen by the team. It will collect and analyze subsurface samples of at least 10g from depths of 10 cm or more. The rover must also document sites using wide-angle panoramas (1:3 height-to-width ratio) with GPS coordinates, elevation, and scale, alongside close-up, high-resolution images. The rover will drop a sample at a designated location for future retrieval during the Reconnaissance and Delivery Mission.

R D O
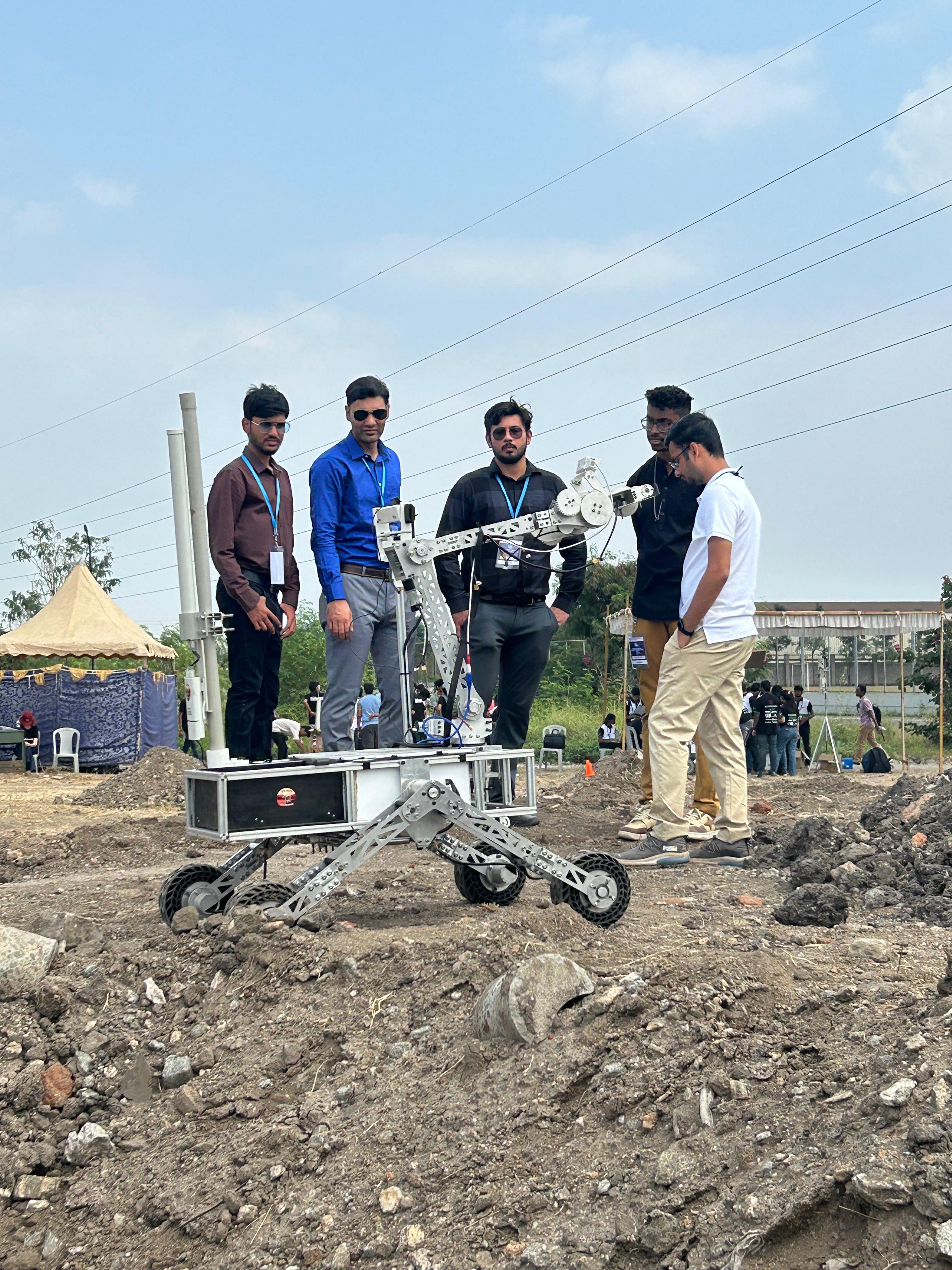
The Reconnaissance and Delivery Operation (RDO) mission challenges the rover to locate, photograph, and document objects scattered within a 500m radius, using GPS for precise positioning. The mission consists of two stages: Reconnaissance, where the rover has 10 minutes to locate and document objects, optionally storing one, and Delivery, a 20-minute task to pick up and deliver objects like tools, containers, or rocks to designated GPS coordinates or markers. The terrain includes sand, rocks, slopes, and boulders, with varying levels of difficulty. Teams are scored based on accuracy in locating, handling, and delivering objects within the time limit.

A U T E X
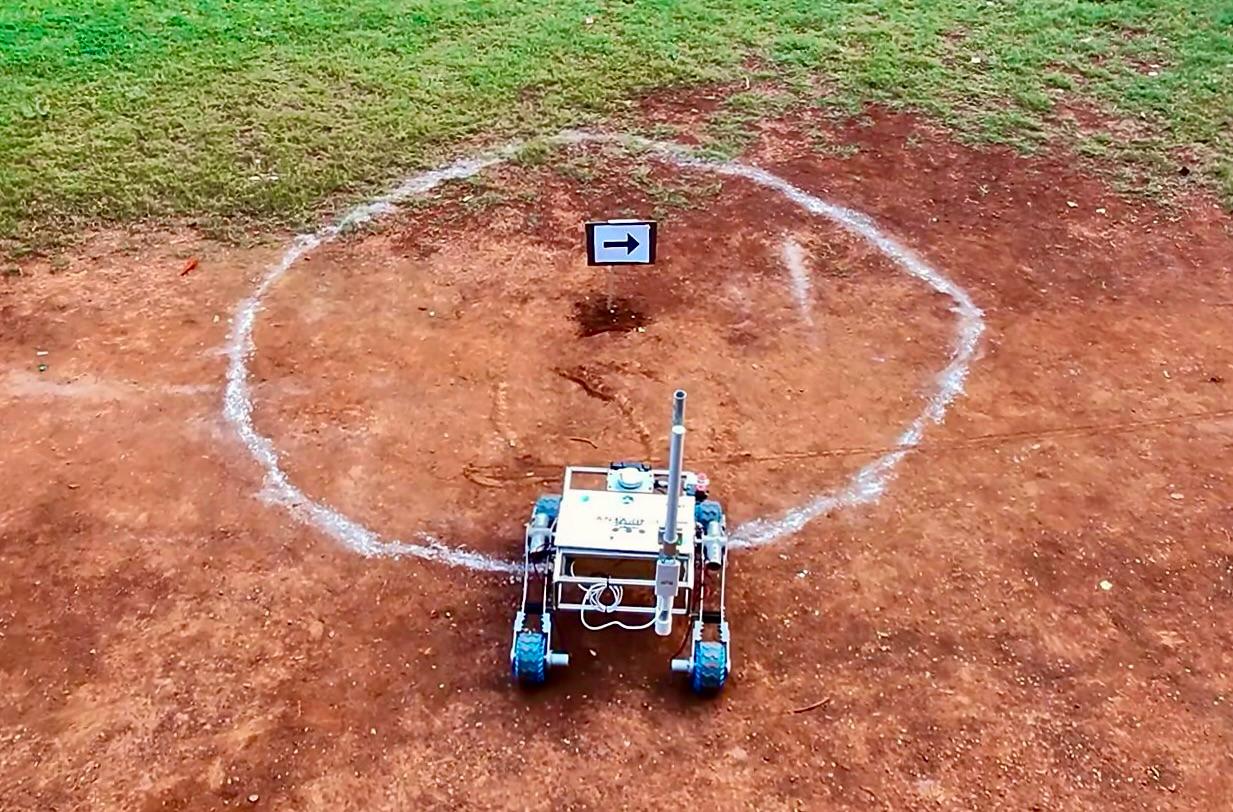
In the autonomous mission, rovers will traverse moderately rugged terrain, navigating between markers using arrow signs on white backgrounds, elevated above the ground. The arrows guide the rover to an endpoint marked by an orange traffic cone. Each arrow is within a 2m radius circle, where the rover must pause for 10 seconds with at least half its body inside the circle before proceeding. The teams should document each arrow sign by collecting its GPS coordinates and the cardinal directions. The teams can collect other data during their autonomous expedition depending on their choice. Using the collected data teams have to prepare a map of the competition site.

I D M O
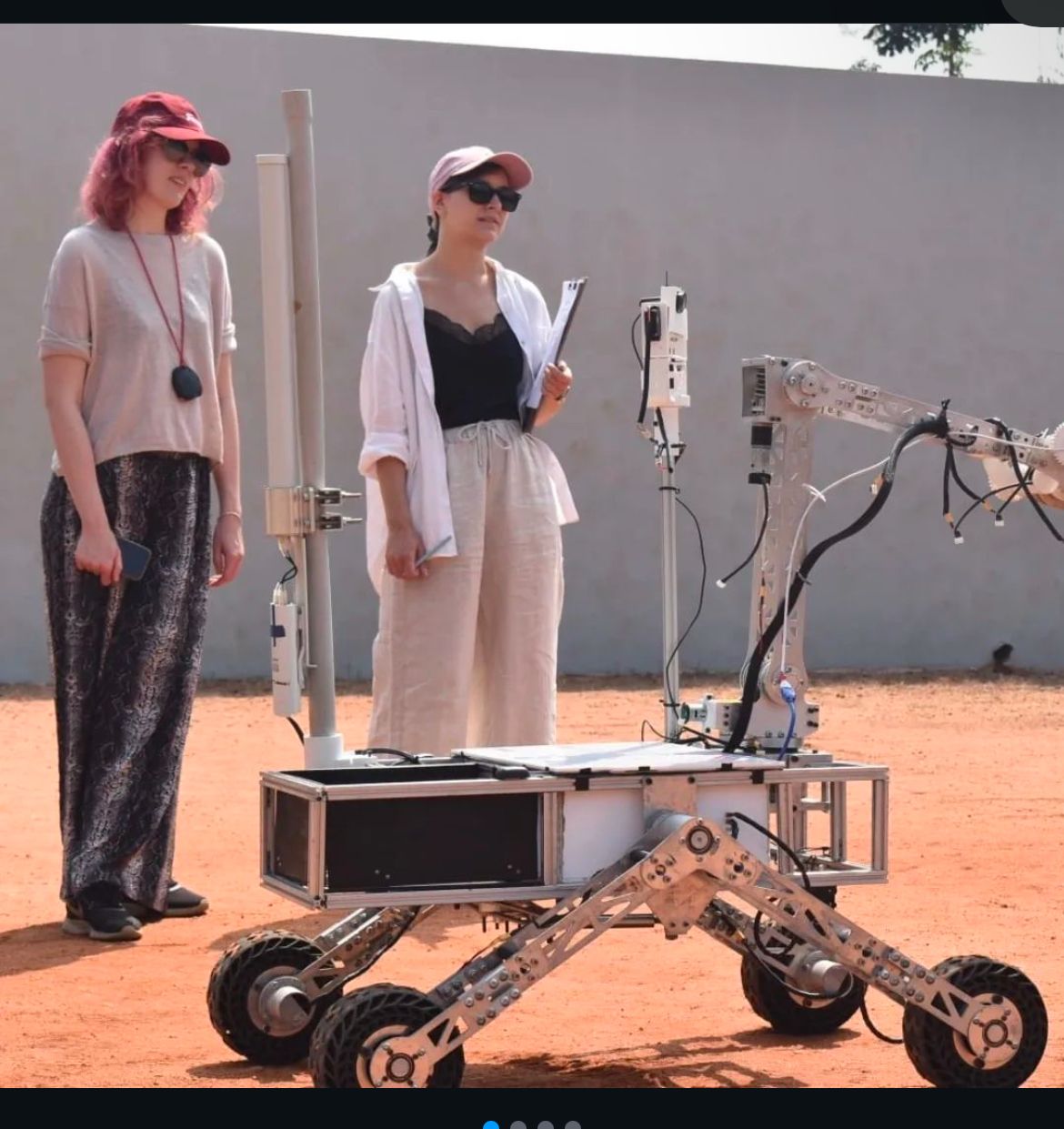
The Instrument Deployment and Maintenance Operation (IDMO) mission involves precise tasks using the rover's robotic arm. It includes two stages: Instrument Maintenance, where the rover picks and places a cache, operates panels, interacts with switches, knobs, and plugs, and performs other fine operations; and Deployment, where the rover retrieves and places sample caches in designated patterns and reads codes from the panel for base station verification.

Participating in the International Rover Challenge (IRC) has been an extraordinary experience that has pushed the boundaries of our technical and collaborative capabilities. From designing and assembling a robust rover to navigating complex challenges like terrain traversal, autonomous navigation, and scientific exploration, the competition has tested every aspect of our engineering expertise. The interdisciplinary collaboration between software, mechanical, and electronics teams fostered innovation and teamwork, while the high-pressure environment has sharpened our problem-solving skills. Competing alongside teams from around the globe provided us with invaluable insights, new perspectives, and a sense of camaraderie that transcended borders. IRC not only allowed us to showcase our rover’s capabilities but also deepened our passion for space exploration and robotics. The event left us inspired, motivated, and eager to tackle even greater challenges in the future, especially after securing the 2nd runner-up position last year. We are determined to push the boundaries of our knowledge and skills, aiming to achieve even greater heights this year.

